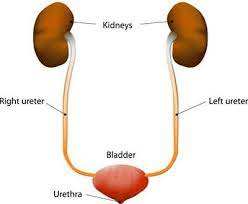
The urinary system’s function is to filter blood and create urine as a waste by-product. The organs of the urinary system include the bladder, kidneys, renal pelvis, ureters, and urethra. The body takes nutrients from food and converts them to energy.
Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer is a common type of cancer that begins in the cells of the bladder. The bladder is a hollow muscular organ in your lower abdomen that stores urine.
Bladder cancer most often begins in the cells (urothelial cells) that line the inside of your bladder.
Symptoms of Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer signs and symptoms may include:
- Blood in urine (hematuria), which may cause urine to appear bright red or cola colored, though sometimes the urine appears normal and blood is detected on a lab test
- Frequent urination
- Painful urination
- Back pain
Causes of Bladder Cancer
- Smoking. Smoking cigarettes, cigars or pipes may increase the risk of bladder cancer by causing harmful chemicals to accumulate in the urine.
- Increasing age.
- Being male.
- Exposure to certain chemicals.
- Previous cancer treatment.
- Chronic bladder inflammation.
- Personal or family history of cancer.
Types of Bladder Cancer
- Urothelial carcinoma. Urothelial carcinoma (or UCC) accounts for about 90% of all bladder cancers. …
- Squamous cell carcinoma. …
- Adenocarcinoma.
Kidney Cancer
Kidney cancer is cancer that begins in the kidneys. Your kidneys are two bean-shaped organs, each about the size of your fist. They’re located behind your abdominal organs, with one kidney on each side of your spine. In adults, renal cell carcinoma is the most common type of kidney cancer.
Wilms tumour or nephroblastoma is a rare type of kidney cancer that is more prevalent among children. One of the first symptoms of Wilms tumour is abdominal swelling.
Symptoms of Kidney Cancer
- Blood in the urine (hematuria)
- Low back pain on one side (not caused by injury)
- A mass (lump) on the side or lower back.
- Fatigue (tiredness)
- Loss of appetite.
- Weight loss not caused by dieting.
- Fever that is not caused by an infection and that doesn’t go away.
Causes of Kidney Cancer
The exact causes of kidney cancer, like many other cancers, are not known. However, we do know that certain things can increase your chances of developing kidney cancer.
- Older Age,
- Smoking,
- Obesity,
- High Blood Pressure,
- Long-Term Dialysis,
- Family History of Kidney Cancer
Types of Kidney Cancer
- Renal cell carcinoma. Renal cell carcinoma is the most common type of adult kidney cancer, making up about 85% of diagnoses. …
- Urothelial carcinoma. This is also called transitional cell carcinoma. …
- Sarcoma. Sarcoma of the kidney is rare. …
- Wilms tumor. …
- Lymphoma.
Cancer of Renal Pelvis or Ureter
Cancer of the renal pelvis or ureter is cancer that forms in the kidney’s pelvis or the tube (ureter) that carries urine from the kidney to the bladder.
Symptoms of Renal Pelvis Cancer
- Blood in the urine.
- A pain in the back that doesn’t go away.
- Extreme tiredness.
- Weight loss with no known reason.
- Painful or frequent urination.
Causes of Renal Pelvis Cancer
- Kidney damage from medicines, especially ones for pain (analgesic nephropathy)
- Exposure to certain dyes and chemicals used to manufacture leather goods, textiles, plastics, and rubber.
- Smoking.
Urethral Cancer
Urethra is the tube through which urine leaves the body. It empties urine from the bladder.
Urethral cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the urethra. There are different types of urethral cancer that begin in cells that line the urethra. A history of bladder cancer can affect the risk of urethral cancer.
Symptoms of Urethral Cancer
- Trouble starting the flow of urine.
- Weak or interrupted (“stop-and-go”) flow of urine.
- Frequent urination, especially at night.
- Incontinence.
- Discharge from the urethra.
- Bleeding from the urethra or blood in the urine.
Causes of Urethral Cancer
- Having a history of bladder cancer.
- Having conditions that cause chronic inflammation in the urethra, including: Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), including human papillomavirus (HPV), especially HPV type 16. Frequent urinary tract infections (UTIs).
